Phosphorus is the second essential macronutrient for plant growth, which plays a vital role in transfer of energy within the various parts of plant and root development for higher water and nutrient use efficiency. Phosphorus (P) is one of the major plant growth-limiting nutrients although it is abundant in soils in both inorganic and organic forms. Phosphate solubilizing micro-organisms are ubiquitous in soils and could play an important role in supplying P to plants in a more environmentally friendly and sustainable manner.
The insoluble P content of fertilisers may be converted to the soluble form by chemical acidulation and biological means. The biological solubilisation of P is a far more environment-friendly option and one that has far reaching effects on the soil environment. The major microbial means by which insoluble P compounds are mobilized is by the production of organic acids. The organic acids that are produced convert insoluble with the net result being enhanced availability of the element to the plant. The type of organic acids produced and their amount affect the amount of P solubilized.
The addition of acid creating microbes enhances the process of P availability; hence EM having acid producing microbes is able to create to increase the process of P availability. The EM contains selected species of microorganisms including lactic acid bacteria (acid producing), yeasts, smaller numbers of photosynthetic bacteria, actinomycetes, fermentative fungi and other types of organisms. All of these are mutually compatible with one another and can coexist in liquid culture. The lactic acid is a strong sterilizing compound enhances decomposition of organic matter. The lactic acid producing bacteria promote the decomposition process and remove undesirable effects of un-decomposed organic material. It improves the physical, chemical and biological environment of the soil (Higa & Parr, 1994). Many researchers have reported that application of EM may enhance the crops yields, increase the bio availability of nutrients. Hussain et al., (2000) reported the agronomic merits of EM in a rice-wheat cropping system. In all cases, the grain and straw yields from EM alone were higher than the controls. The EM applied in combination with FYM caused a significant increase in nutrient uptake by the grain and straw of each crop. The uptake of NPK by both crops was higher for EM alone than for the control. Similar supportive conclusions have been reported by Kishore (2000), Xu et al., (2000) and Yamada & Xu (2001). The combined application of P with FYM and EM help to improve P solubility from P Fertiliser and decrease the time span of their decomposition (Sharif et al., 2014 and Ahmad et al.).
Keeping in view the importance of P in crop production and its solubility enhancement through biological means, studies were conducted to determine the effects of Rock Phosphate and FYM applied with and without EM, on yields and plant P uptake of wheat and their residual effect on a subsequent sunflower crop.
Trial demonstrating the Effect of EM on P Solubility and Uptake to the Plant
In a trial conducted at the University of Agriculture, Peshawar, Pakistan on the Effect of Rock Phosphate and Farmyard Manure Applied with Effective Microorganisms on the Yield and Nutrient Uptake of Wheat and Sunflower Crops, The trial concluded, that application of rock phosphate with farm yard manure and effective microorganisms, have potential to improve crop yields, and plant N and P uptake, on a sustainable basis as their effects are longer lived.
I have expanded on the results in greater detail below.
Soil P levels post-Harvest
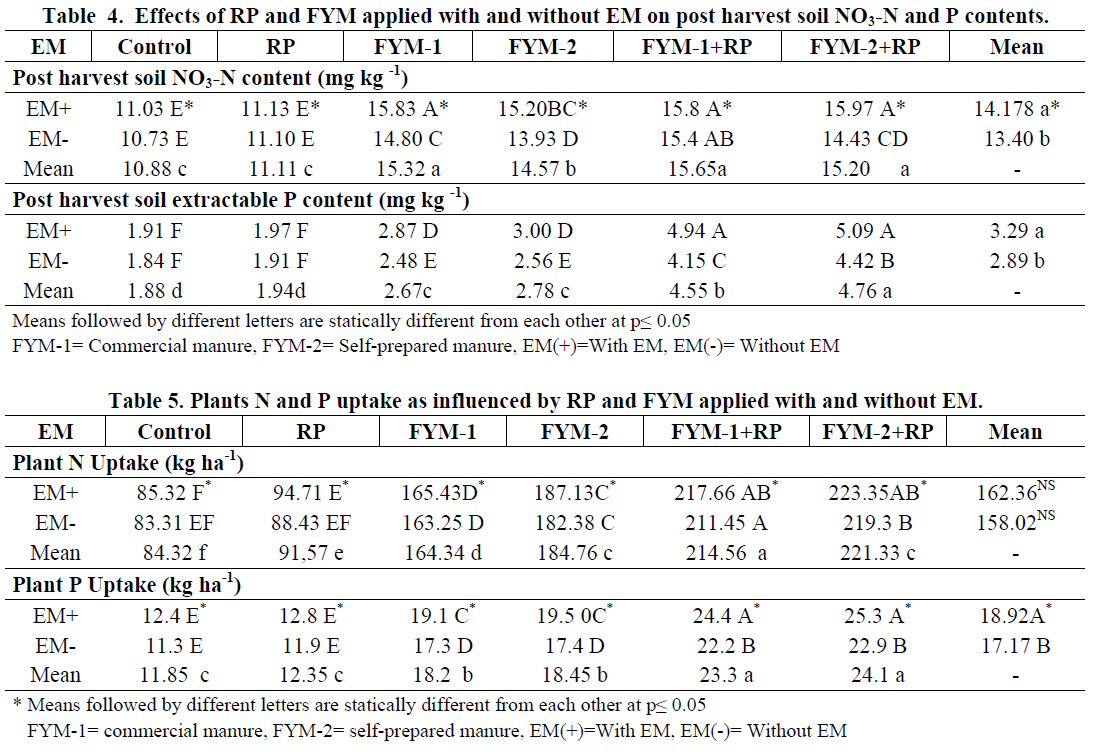
Table 4. below shows that the extractable P content recorded after the harvest of crop showed significant (p≤0.01) variations among the EM levels, various combinations of FYM and RP and interaction between EM and RP and FYM combination. The results of EM levels in main plot showed that plots with EM showed comparatively higher extractable soil P content than EM.
P uptake by the Plants
The results (Table 5) showed comparatively higher plant N and P uptakes with the application of EM. Data regarding Plants P uptake by wheat plants revealed significant (p≤0.05) increases by all of the applications including EM. The interaction of EM levels (main-plot) and RP and FYM combinations (sub plot) also showed significant (p≤0.05) effect on plant P uptake of wheat.
Total Yield
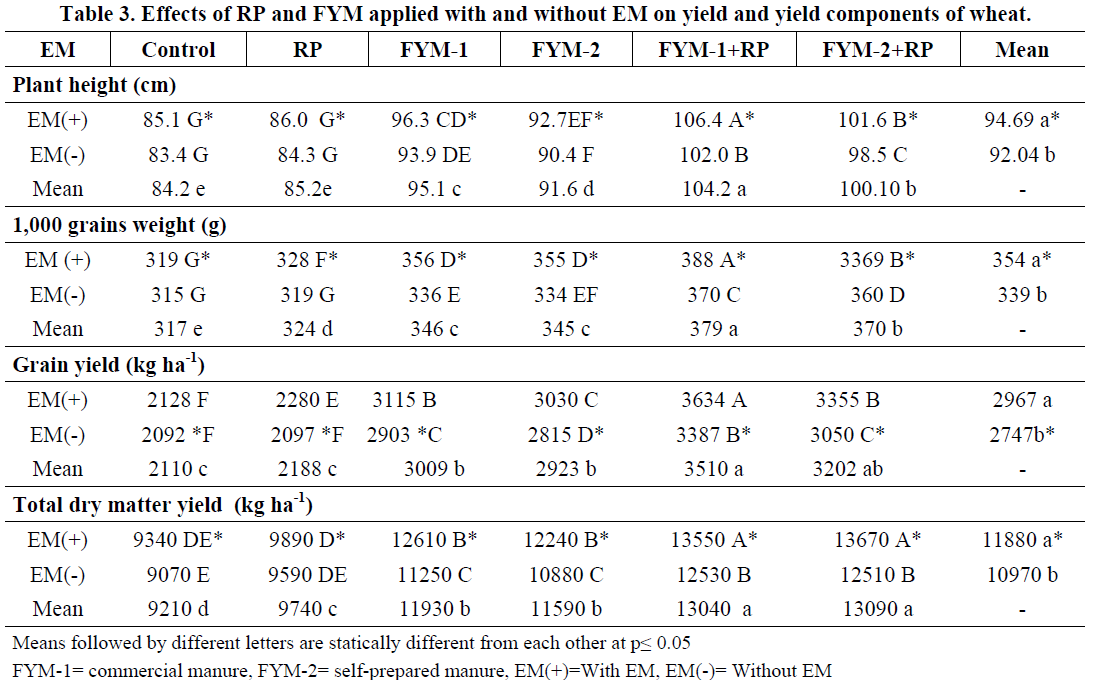
The interaction between EM and RP applied with FYM was significant (p≤0.05) for head diameter, grain yield, while non-significant for plant height and total dry matter yield of sunflower. The residual effect of EM was significant (p≤0.05) for N and P uptake by sunflower plants. These results suggest that solubility of P may be enhanced from RP through application with FYM and EM, which has the potential to improve plants N and P uptake and crops yields on sustainable basis.
Source link













![[Video] Easy Aerial’s Drone-in-a-Box Automates Crop Scouting](../ext/resources/images/2022/April/Easy-Aerials-Drone-in-a-Box-Automates-Crop-Scouting.jpg)